Quantifying the Quality of Haptic Interfaces
Shape-Changing Haptic Interfaces
Generating Clear Vibrotactile Cues with Magnets Embedded in a Soft Finger Sheath
Salient Full-Fingertip Haptic Feedback Enabled by Wearable Electrohydraulic Actuation
Cutaneous Electrohydraulic (CUTE) Wearable Devices for Pleasant Broad-Bandwidth Haptic Cues
Modeling Finger-Touchscreen Contact during Electrovibration
Perception of Ultrasonic Friction Pulses
Vibrotactile Playback for Teaching Sensorimotor Skills in Medical Procedures
CAPT Motor: A Two-Phase Ironless Motor Structure
4D Intraoperative Surgical Perception: Anatomical Shape Reconstruction from Multiple Viewpoints
Visual-Inertial Force Estimation in Robotic Surgery
Enhancing Robotic Surgical Training
AiroTouch: Naturalistic Vibrotactile Feedback for Large-Scale Telerobotic Assembly
Optimization-Based Whole-Arm Teleoperation for Natural Human-Robot Interaction
Finger-Surface Contact Mechanics in Diverse Moisture Conditions
Computational Modeling of Finger-Surface Contact
Perceptual Integration of Contact Force Components During Tactile Stimulation
Dynamic Models and Wearable Tactile Devices for the Fingertips
Novel Designs and Rendering Algorithms for Fingertip Haptic Devices
Dimensional Reduction from 3D to 1D for Realistic Vibration Rendering
Prendo: Analyzing Human Grasping Strategies for Visually Occluded Objects
Learning Upper-Limb Exercises from Demonstrations
Minimally Invasive Surgical Training with Multimodal Feedback and Automatic Skill Evaluation
Efficient Large-Area Tactile Sensing for Robot Skin
Haptic Feedback and Autonomous Reflexes for Upper-limb Prostheses
Gait Retraining
Modeling Hand Deformations During Contact
Intraoperative AR Assistance for Robot-Assisted Minimally Invasive Surgery
Immersive VR for Phantom Limb Pain
Visual and Haptic Perception of Real Surfaces
Haptipedia
Gait Propulsion Trainer
TouchTable: A Musical Interface with Haptic Feedback for DJs
Exercise Games with Baxter
Intuitive Social-Physical Robots for Exercise
How Should Robots Hug?
Hierarchical Structure for Learning from Demonstration
Fabrication of HuggieBot 2.0: A More Huggable Robot
Learning Haptic Adjectives from Tactile Data
Feeling With Your Eyes: Visual-Haptic Surface Interaction
S-BAN
General Tactile Sensor Model
Insight: a Haptic Sensor Powered by Vision and Machine Learning
Insight: a Haptic Sensor Powered by Vision and Machine Learning
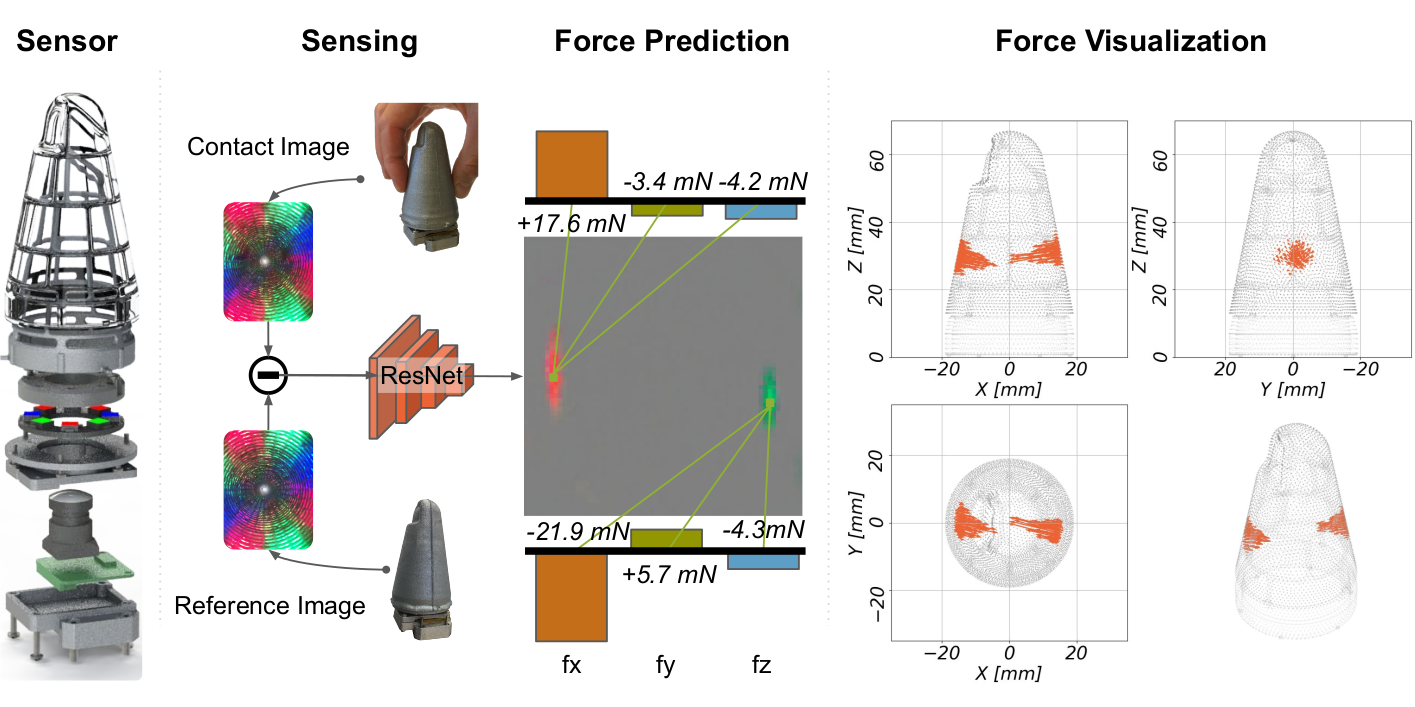
Robots need detailed haptic sensing that covers their complex surfaces to learn effective behaviors in unstructured environments. However, state-of-the-art sensors tend to focus on improving precision and sensitivity, increasing taxel density, or enlarging the sensed area rather than prioritizing system robustness and the usability of the sensed haptic information. By considering the goals and constraints from a fresh perspective, we have designed a robust, soft, low-cost, vision-based, thumb-sized 3D haptic sensor named Insight; it continually supplies the host robot with a directional force-distribution map over its entire conical sensing surface [].
Insight uses an internal monocular camera, photometric stereo, and structured light to detect the 3D deformation of the easily replaceable flexible outer shell, which is molded in a single layer over a stiff frame to guarantee sensitivity, robustness, and a soft contact surface []. The force information is inferred by a deep-neural-network-based machine-learning method that maps images to the spatial distribution of 3D contact force (normal and shear), including numerous distinct contacts with widely varying contact areas [
].
Extensive experiments show that Insight has an overall spatial resolution of 0.4 mm, force magnitude accuracy around 0.03 N, and force direction accuracy around 5 degrees over a range of 0.03-2 N. It is sensitive enough to feel its own orientation relative to gravity, and its tactile fovea can be used to sense object shapes. The presented hardware and software design concepts can be extended to achieve robust and usable tactile sensing on a wide variety of robot parts with different shapes and sensing requirements. Ongoing work aims to reduce Insight's size, increase its framerate, and add other haptic sensing modalities such as vibration.
Members
Publications


