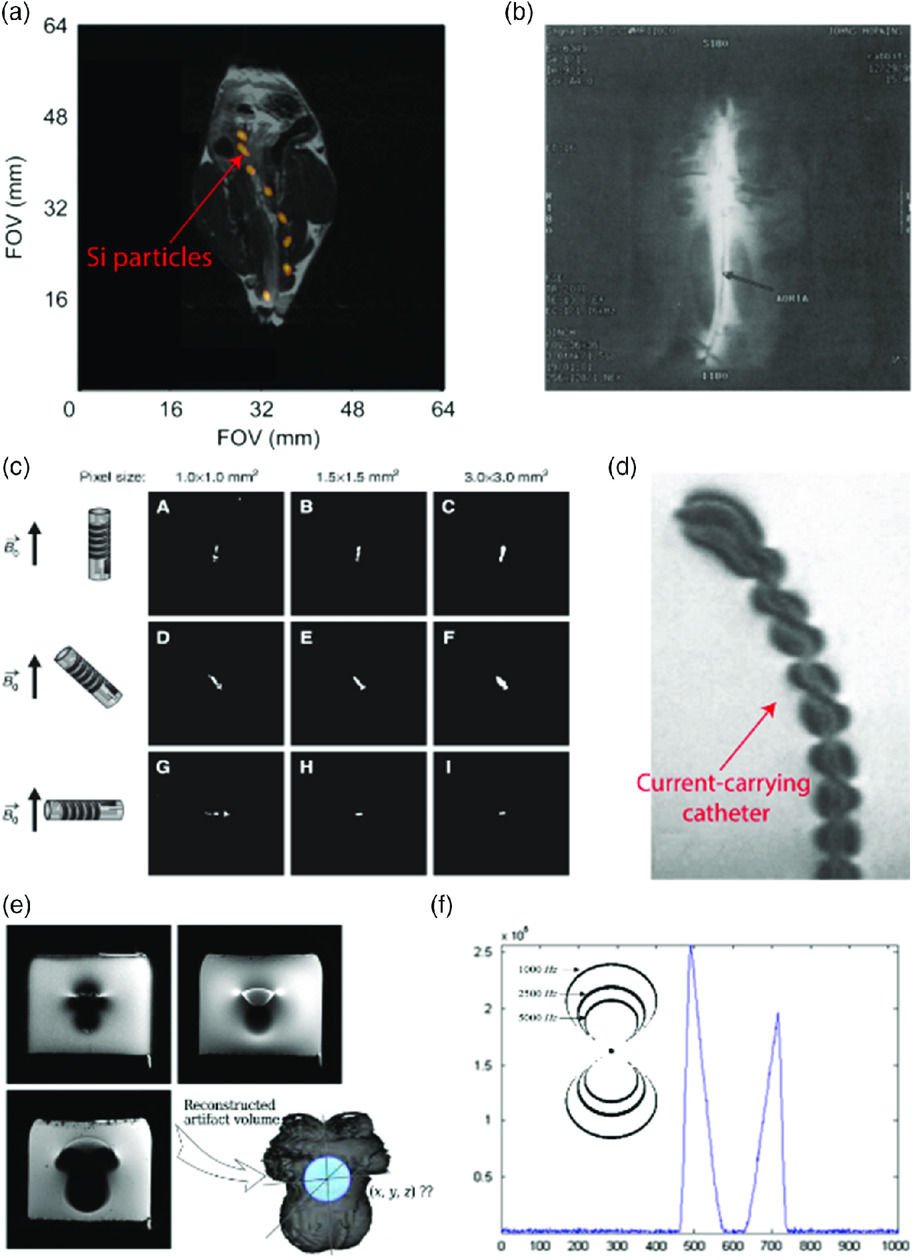
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system–driven medical robotics is an emerging field that aims to use clinical MRI systems not only for medical imaging but also for actuation, localization, and control of medical robots. Submillimeter scale resolution of MR images for soft tissues combined with the electromagnetic gradient coil–based magnetic actuation available inside MR scanners can enable theranostic applications of medical robots for precise image‐guided minimally invasive interventions. MRI‐driven robotics typically does not introduce new MRI instrumentation for actuation but instead focuses on converting already available instrumentation for robotic purposes. To use the advantages of this technology, various medical devices such as untethered mobile magnetic robots and tethered active catheters have been designed to be powered magnetically inside MRI systems. Herein, the state‐of‐the‐art progress, challenges, and future directions of MRI‐driven medical robotic systems are reviewed.
| Author(s): | Erin, Onder and Boyvat, Mustafa and Tiryaki, Mehmet Efe and Phelan, Martin and Sitti, Metin |
| Journal: | Advanced Intelligent Systems |
| Volume: | 2 |
| Number (issue): | 2 |
| Pages: | 1900110 |
| Year: | 2020 |
| Project(s): | |
| Bibtex Type: | Article (article) |
| DOI: | 10.1002/aisy.201900110 |
| Electronic Archiving: | grant_archive |
BibTex
@article{erin2020magnetic,
title = {Magnetic resonance imaging system-driven medical robotics},
journal = {Advanced Intelligent Systems},
abstract = {Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system–driven medical robotics is an emerging field that aims to use clinical MRI systems not only for medical imaging but also for actuation, localization, and control of medical robots. Submillimeter scale resolution of MR images for soft tissues combined with the electromagnetic gradient coil–based magnetic actuation available inside MR scanners can enable theranostic applications of medical robots for precise image‐guided minimally invasive interventions. MRI‐driven robotics typically does not introduce new MRI instrumentation for actuation but instead focuses on converting already available instrumentation for robotic purposes. To use the advantages of this technology, various medical devices such as untethered mobile magnetic robots and tethered active catheters have been designed to be powered magnetically inside MRI systems. Herein, the state‐of‐the‐art progress, challenges, and future directions of MRI‐driven medical robotic systems are reviewed.},
volume = {2},
number = {2},
pages = {1900110},
year = {2020},
slug = {erin2020magnetic},
author = {Erin, Onder and Boyvat, Mustafa and Tiryaki, Mehmet Efe and Phelan, Martin and Sitti, Metin}
}