A Hierarchical 3D TiO2/Ni Nanostructure as an Efficient Hole‐Extraction and Protection Layer for GaAs Photoanodes
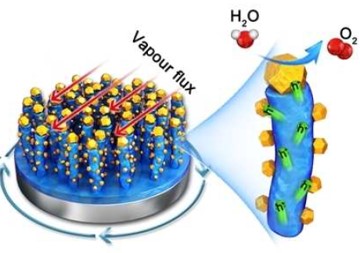
Photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting is a promising clean route to hydrogen fuel. The best‐performing materials (III/V semiconductors) require surface passivation, as they are liable to corrosion, and a surface co‐catalyst to facilitate water splitting. At present, optimal design combining photoelectrodes with oxygen evolution catalysts remains a significant materials challenge. Here, we demonstrate that nickel‐coated amorphous three‐dimensional (3D) TiO2 core‐shell nanorods on a TiO2 thin film function as an efficient hole‐extraction layer and serve as a protection layer for the GaAs photoanode. Transient‐absorption spectroscopy (TAS) demonstrated the role of nickel‐coated (3D) TiO2 core‐shell nanorods in prolonging photogenerated charge lifetimes in GaAs, resulting in a higher catalytic activity. This strategy may open the potential of utilizing this low‐cost (3D) nanostructured catalyst for decorating narrow‐band‐gap semiconductor photoanodes for PEC water splitting devices.
| Author(s): | Alqahtani, M. and Kafizas, A. and Sathasivam, S. and Ebaid, M. and Cui, F. and Alymani, A. and Jeong, H.-H, and Lee, T.-C. and Fischer, P. and Parkin, I. and Grätzel, M. and Wu, J. |
| Journal: | ChemSusChem |
| Volume: | 13 |
| Number (issue): | 22 |
| Pages: | 6028--6036 |
| Year: | 2020 |
| Month: | September |
| Day: | 28 |
| Bibtex Type: | Article (article) |
| DOI: | 10.1002/cssc.202002004 |
| URL: | https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/cssc.202002004 |
| Electronic Archiving: | grant_archive |
BibTex
@article{2020chemsuschem,
title = {A Hierarchical 3D TiO2/Ni Nanostructure as an Efficient Hole‐Extraction and Protection Layer for GaAs Photoanodes},
journal = {ChemSusChem},
abstract = {Photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting is a promising clean route to hydrogen fuel. The best‐performing materials (III/V semiconductors) require surface passivation, as they are liable to corrosion, and a surface co‐catalyst to facilitate water splitting. At present, optimal design combining photoelectrodes with oxygen evolution catalysts remains a significant materials challenge. Here, we demonstrate that nickel‐coated amorphous three‐dimensional (3D) TiO2 core‐shell nanorods on a TiO2 thin film function as an efficient hole‐extraction layer and serve as a protection layer for the GaAs photoanode. Transient‐absorption spectroscopy (TAS) demonstrated the role of nickel‐coated (3D) TiO2 core‐shell nanorods in prolonging photogenerated charge lifetimes in GaAs, resulting in a higher catalytic activity. This strategy may open the potential of utilizing this low‐cost (3D) nanostructured catalyst for decorating narrow‐band‐gap semiconductor photoanodes for PEC water splitting devices.},
volume = {13},
number = {22},
pages = {6028--6036},
month = sep,
year = {2020},
slug = {2020chemsuschem},
author = {Alqahtani, M. and Kafizas, A. and Sathasivam, S. and Ebaid, M. and Cui, F. and Alymani, A. and Jeong, H.-H and Lee, T.-C. and Fischer, P. and Parkin, I. and Gr{\"a}tzel, M. and Wu, J.},
url = {https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/cssc.202002004},
month_numeric = {9}
}


