2023
ei
Jenny, D.
Navigating the Ocean of Biases: Political Bias Attribution in Language Models via Causal Structures
ETH Zurich, Switzerland, November 2023, external supervision (thesis)
rm
Keplinger, C. M., Acome, E. L., Kellaris, N. A., Mitchell, S. K.
Hydraulically Amplified Self-healing Electrostatic Actuators
(US Patent 11795979B2), October 2023 (patent)
rm
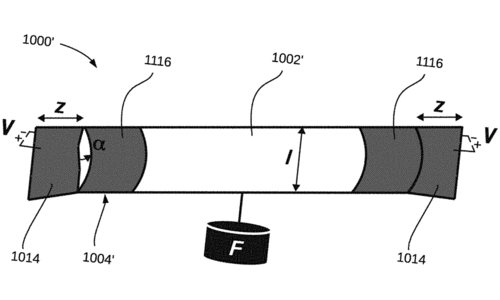
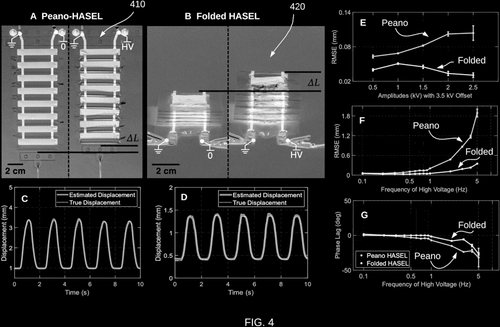
Keplinger, C. M., Wang, X., Mitchell, S. K.
High Strain Peano Hydraulically Amplified Self-Healing Electrostatic (HASEL) Transducers
(US Patent App. 18/138,621), August 2023 (patent)
rm
Correll, N., Ly, K. D., Kellaris, N. A., Keplinger, C. M.
Capacitive Self-Sensing for Electrostatic Transducers with High Voltage Isolation
(US Patent App. 17/928,453), June 2023 (patent)
rm
Keplinger, C. M., Wang, X., Mitchell, S. K.
High Strain Peano Hydraulically Amplified Self-healing Electrostatic (HASEL) Transducers
(US Patent 11635094), April 2023 (patent)
dlg
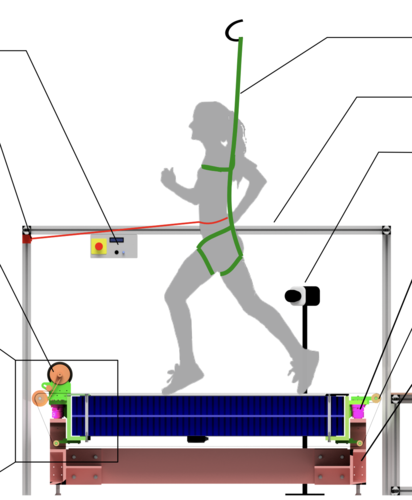
Sarvestani, A., Ruppert, F., Badri-Spröwitz, A.
An Open-Source Modular Treadmill for Dynamic Force Measurement with Load Dependant Range Adjustment
2023 (unpublished) Submitted
ei
Jin, Z., Mihalcea, R.
Natural Language Processing for Policymaking
In Handbook of Computational Social Science for Policy, pages: 141-162, 7, (Editors: Bertoni, E. and Fontana, M. and Gabrielli, L. and Signorelli, S. and Vespe, M.), Springer International Publishing, 2023 (inbook)
pi
Wang, T., Hu, W., Sitti, M.
Tube-shaped robotic device with anisotropic surface structure
2023, US Patent App. 18/133,104 (patent)
pi
Drotlef, D., Sitti, M., Amjadi, M.
Carrier, use of a carrier, method of activating a carrier and method of making a carrier
2023, US Patent App. 16/500,442 (patent)
pi
Sitti, M., Aksak, B.
Microfibers with mushroom-shaped tips for optimal adhesion
2023, US Patent 11,613,674 (patent)
pi
Zhang, J., Ren, Z., Hu, W., Sitti, M.
Method of fabricating a magnetic deformable machine and deformable 3D magnetic machine
2023, US Patent App. 18/020,161 (patent)
pi
Son, D., Ugurlu, M., Bluemer, P., Sitti, M.
Magnetic trap system and method of navigating a microscopic device
2023, US Patent App. 17/871,598 (patent)
pi
Sitti, M., Drotlef, D., Liimatainen, V.
A Liquid Repellent Fibrillar Dry Adhesive Material and a Method of Producing the Same
2023, US Patent App. 17/785,452 (patent)
pi
Sitti, M., Son, D., Dong, X.
Simultaneous calibration method for magnetic localization and actuation systems
2023, US Patent 11,717,142 (patent)
pi
M Sitti, M. M. B. A.
Dry adhesives and methods for making dry adhesives
2023, US Patent 11,773,298, 2023 (patent)
2022
pi
Metin Sitti, Michael Murphy, Burak Aksak
DRY ADHESIVES AND METHODS FOR MAKING DRY ADHESIVES
December 2022, US Patent App. 17/895,334, 2022 (patent)
rm
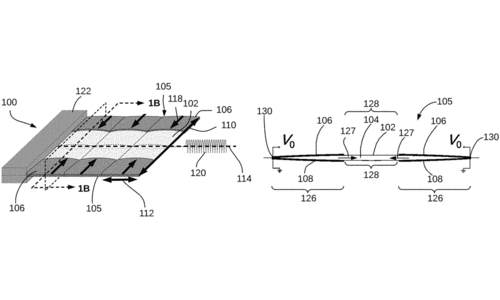
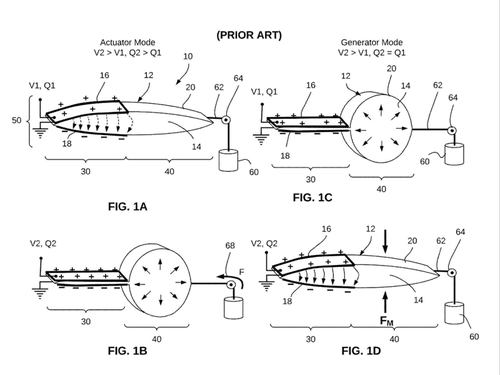
Keplinger, C. M., Acome, E. L., Kellaris, N. A., Mitchell, S. K., Morrissey, T. G.
Hydraulically Amplified Self-healing Electrostatic Transducers Harnessing Zipping Mechanism
(US Patent 11486421B2), November 2022 (patent)
pf
Qiu, T., Jeong, M., Goyal, R., Kadiri, V., Sachs, J., Fischer, P.
Magnetic Micro-/Nanopropellers for Biomedicine
In Field-Driven Micro and Nanorobots for Biology and Medicine, pages: 389-410, 16, (Editors: Sun, Y. and Wang, X. and Yu, J.), Springer, Cham, 2022 (inbook)
re
Lieder, F., Prentice, M.
Life Improvement Science
In Encyclopedia of Quality of Life and Well-Being Research, Springer, November 2022 (inbook)
rm
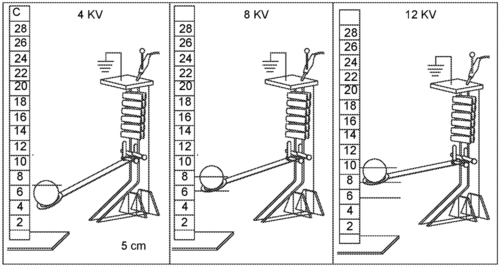
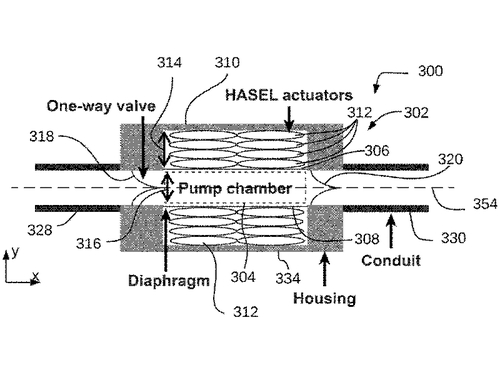
Mitchell, S. K., Acome, E. L., Keplinger, C. M.
Hydraulically Amplified Self-Healing Electrostatic (HASEL) Pumps
(US Patent App. 17/635,339), October 2022 (patent)
ei
Schölkopf, B.
Causality, causal digital twins, and their applications
Machine Learning for Science: Bridging Data-Driven and Mechanistic Modelling (Dagstuhl Seminar 22382), (Editors: Berens, Philipp and Cranmer, Kyle and Lawrence, Neil D. and von Luxburg, Ulrike and Montgomery, Jessica), September 2022 (talk)
rm
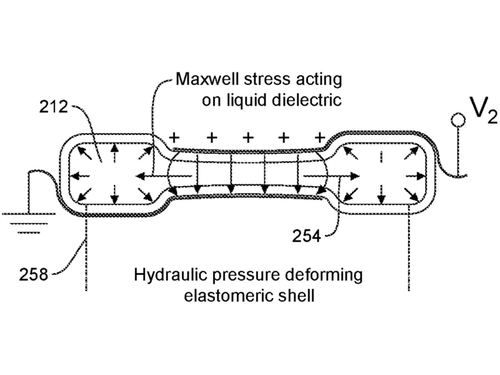
Keplinger, C. M., Acome, E. L., Kellaris, N. A., Mitchell, S. K.
Hydraulically Amplified Self-healing Electrostatic Actuators
(US Patent 11408452), August 2022 (patent)
rm
Keplinger, C. M., Mitchell, S. K., Kellaris, N. A., Rothemund, P.
Composite Layering of Hydraulically Amplified Self-Healing Electrostatic Transducers
(US Patent App. 17436455), May 2022 (patent)
ei
Peters, J., Bauer, S., Pfister, N.
Causal Models for Dynamical Systems
In Probabilistic and Causal Inference: The Works of Judea Pearl, pages: 671-690, 1, Association for Computing Machinery, 2022 (inbook)
ei
plg
Karimi, A. H., von Kügelgen, J., Schölkopf, B., Valera, I.
Towards Causal Algorithmic Recourse
In xxAI - Beyond Explainable AI: International Workshop, Held in Conjunction with ICML 2020, July 18, 2020, Vienna, Austria, Revised and Extended Papers, pages: 139-166, (Editors: Holzinger, Andreas and Goebel, Randy and Fong, Ruth and Moon, Taesup and Müller, Klaus-Robert and Samek, Wojciech), Springer International Publishing, 2022 (inbook)
ei
Salewski, L., Koepke, A. S., Lensch, H. P. A., Akata, Z.
CLEVR-X: A Visual Reasoning Dataset for Natural Language Explanations
In xxAI - Beyond Explainable AI: International Workshop, Held in Conjunction with ICML 2020, July 18, 2020, Vienna, Austria, Revised and Extended Papers, pages: 69-88, (Editors: Holzinger, Andreas and Goebel, Randy and Fong, Ruth and Moon, Taesup and Müller, Klaus-Robert and Samek, Wojciech), Springer International Publishing, 2022 (inbook)
ei
Schölkopf, B.
Causality for Machine Learning
In Probabilistic and Causal Inference: The Works of Judea Pearl, pages: 765-804, 1, Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 2022 (inbook)
2021
ev
Strecke, M., Stückler, J.
Physically Plausible Tracking & Reconstruction of Dynamic Objects
KIT Science Week Scientific Conference & DGR-Days 2021, October 2021 (talk)
ps
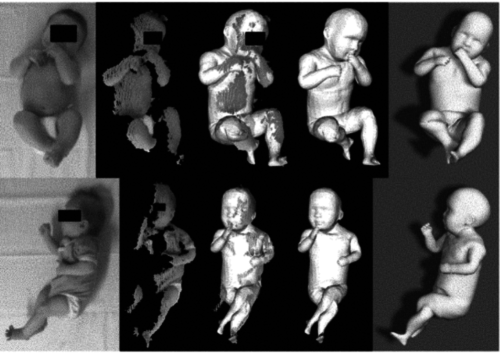
Hesse, N., Pujades, S., Romero, J., Black, M.
Skinned multi-infant linear body model
(US Patent 11,127,163, 2021), September 2021 (patent)
rm
Purnendu, , Novack, S., Acome, E., Alistar, M., Keplinger, C., Gross, M. D., Bruns, C., Leithinger, D.
Electriflow: Augmenting Books With Tangible Animation Using Soft Electrohydraulic Actuators
In ACM SIGGRAPH 2021 Labs, pages: 1-2, Association for Computing Machinery, SIGGRAPH 2021, August 2021 (inbook)
re
Heindrich, L., Consul, S., Stojcheski, J., Lieder, F.
Improving Human Decision-Making by Discovering Efficient Strategies for Hierarchical Planning
Tübingen, Germany, The first edition of Life Improvement Science Conference, June 2021 (talk) Accepted
rm
Keplinger, C. M., Acome, E. L., Kellaris, N. A., Mitchell, S. K.
Hydraulically amplified self-healing electrostatic actuators
(US Patent 10995779), May 2021 (patent)
rm
Keplinger, C. M., Acome, E. L., Kellaris, N. A., Mitchell, S. K., Morrissey, T. G.
Hydraulically Amplified Self-Healing Electrostatic Transducers Harnessing Zipping Mechanism
(US Patent 20210003149A1), January 2021 (patent)
al
hi
Sun, H., Martius, G., Kuchenbecker, K. J.
Sensor Arrangement for Sensing Forces and Methods for Fabricating a Sensor Arrangement and Parts Thereof
(PCT/EP2021/050230), Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, Max Planck Ring 4, January 2021 (patent)
al
hi
Sun, H., Martius, G., Kuchenbecker, K. J.
Method for force inference, method for training a feed-forward neural network, force inference module, and sensor arrangement
(PCT/EP2021/050231), Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, Max Planck Ring 4, January 2021 (patent)
pi
Sitti, M., Son, D.
Magnetically actuated capsule endoscope, magnetic field generating and sensing apparatus and method of actuating a magnetically actuated capsule endoscope
2021, US Patent App. 16/617,348 (patent)
pf
Wu, Z., Qiu, T., Fischer, P.
Slippery micropropellers penetrate the vitreous humor
(US20210170056A1), 2021 (patent)
pi
Sitti, M., Son, D., Bluemler, P.
Magnetic trap system and method of navigating a microscopic device
2021, EP Prio. Patent App. 21 187 691.7 (patent)
pi
Sitti, M., Zhang, J., Ren, Z., Hu, W.
Three-dimensional assembly based microfabrication strategy for magnetic soft machines
2021, International App. PCT/EP2021/071716 (patent)
pf
Qiu, T., Fischer, P.
Magnetic field generator
(US20210228298A1), 2021 (patent)
pi
Sitti, M., Liimatainen, V.
Method of making one or more fibrils, computer implemented method of simulating an adhesive force of one or more fibrils and fibril
2021, EP Prio. Patent App. 21 162 253.5 (mpi_year_book)
pi
Sitti, M., Alapan, Y., Karacakol, A.
Heat assisted magnetic programming of soft materials
2021, International App. PCT/EP2021/060313 (patent)
pi
Sitti, M., Bozuyuk, U., Ceylan, H., Yasa, O., Yasa, I. C.
Light-triggered Drug Release from 3D-printed Magnetic Chitosan Microswimmers
2021, US Patent App. 17/274215, Feb.2021 (patent)
ei
hi
ps
pi
rm
Scientific Report 2016 - 2021
2021 (mpi_year_book)
minibot
Chu, X., Wang, W., Müller, J., Schöning, H. V., Liu, Y., Weigand, B.
Turbulence Modulation and Energy Transfer in Turbulent Channel Flow Coupled with One-Side Porous Media
In High Performance Computing in Science and Engineering’20, pages: 373-386, Springer, 2021 (incollection)
2020
mms
Nacke, R.
Voltage dependent interfacial magnetism in multilayer systems
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, December 2020 (thesis)
hi
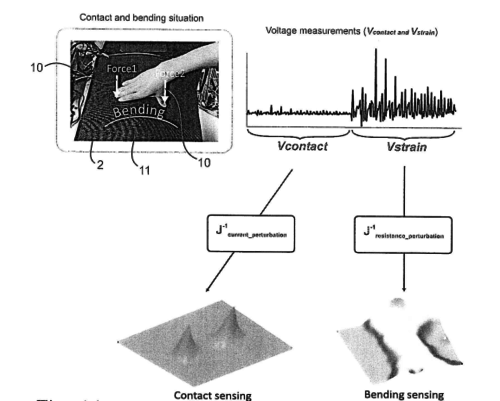
Lee, H., Kuchenbecker, K. J.
System and Method for Simultaneously Sensing Contact Force and Lateral Strain
(EP20000480.2), December 2020 (patent)
al
hi
zwe-rob
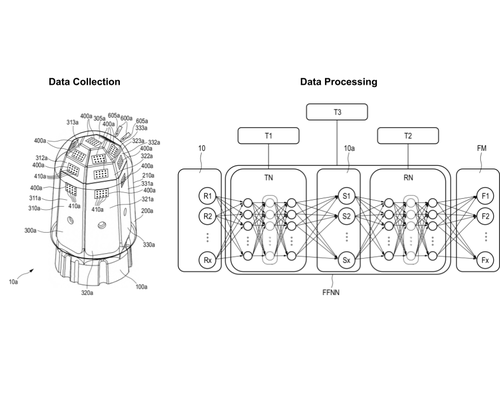
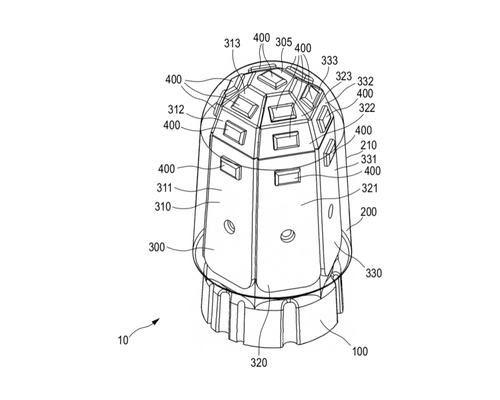
Sun, H., Martius, G., Lee, H., Spiers, A., Fiene, J.
Method for Force Inference of a Sensor Arrangement, Methods for Training Networks, Force Inference Module and Sensor Arrangement
(PCT/EP2020/083261), Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, Max Planck Ring 4, November 2020 (patent)
al
hi
zwe-rob
Spiers, A., Sun, H., Lee, H., Martius, G., Fiene, J., Seo, W. H.
Sensor Arrangement for Sensing Forces and Method for Farbricating a Sensor Arrangement
(PCT/EP2020/083260), November 2020 (patent)