2023
sf
Barocas, S., Hardt, M., Narayanan, A.
Fairness in Machine Learning: Limitations and Opportunities
MIT Press, December 2023 (book)
ei
Jenny, D.
Navigating the Ocean of Biases: Political Bias Attribution in Language Models via Causal Structures
ETH Zurich, Switzerland, November 2023, external supervision (thesis)
dlg
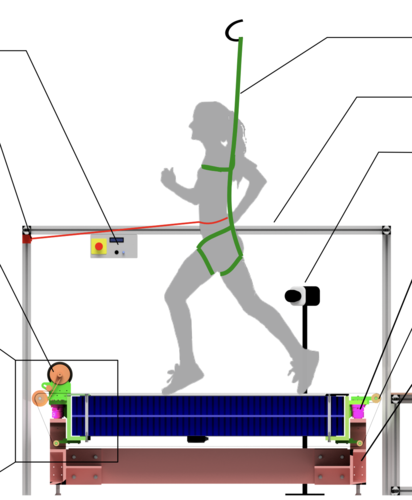
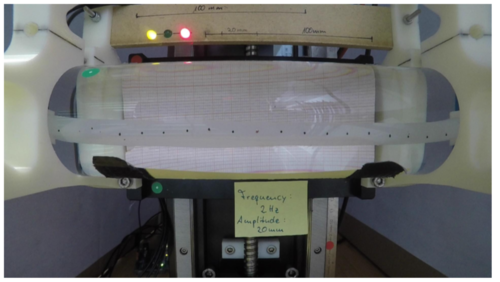
Sarvestani, A., Ruppert, F., Badri-Spröwitz, A.
An Open-Source Modular Treadmill for Dynamic Force Measurement with Load Dependant Range Adjustment
2023 (unpublished) Submitted
2022
ei
Biester, L., Demszky, D., Jin, Z., Sachan, M., Tetreault, J., Wilson, S., Xiao, L., Zhao, J.
Proceedings of the Second Workshop on NLP for Positive Impact (NLP4PI)
Association for Computational Linguistics, December 2022 (proceedings)
ei
Schölkopf, B.
Causality, causal digital twins, and their applications
Machine Learning for Science: Bridging Data-Driven and Mechanistic Modelling (Dagstuhl Seminar 22382), (Editors: Berens, Philipp and Cranmer, Kyle and Lawrence, Neil D. and von Luxburg, Ulrike and Montgomery, Jessica), September 2022 (talk)
sf
Hardt, M., Recht, B.
Patterns, Predictions, and Actions: Foundations of Machine Learning
Princeton University Press, August 2022 (book)
ei
Schölkopf, B., Uhler, C., Zhang, K.
Proceedings of the First Conference on Causal Learning and Reasoning (CLeaR 2022)
177, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, PMLR, April 2022 (proceedings)
2021
ev
Strecke, M., Stückler, J.
Physically Plausible Tracking & Reconstruction of Dynamic Objects
KIT Science Week Scientific Conference & DGR-Days 2021, October 2021 (talk)
ei
Field, A., Prabhumoye, S., Sap, M., Jin, Z., Zhao, J., Brockett, C.
Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on NLP for Positive Impact
Association for Computational Linguistics, August 2021 (proceedings)
re
Heindrich, L., Consul, S., Stojcheski, J., Lieder, F.
Improving Human Decision-Making by Discovering Efficient Strategies for Hierarchical Planning
Tübingen, Germany, The first edition of Life Improvement Science Conference, June 2021 (talk) Accepted
pi
Sitti, M., Liimatainen, V.
Method of making one or more fibrils, computer implemented method of simulating an adhesive force of one or more fibrils and fibril
2021, EP Prio. Patent App. 21 162 253.5 (mpi_year_book)
ei
Belousov, B., H., A., Klink, P., Parisi, S., Peters, J.
Reinforcement Learning Algorithms: Analysis and Applications
883, Studies in Computational Intelligence, Springer International Publishing, 2021 (book)
ei
hi
ps
pi
rm
Scientific Report 2016 - 2021
2021 (mpi_year_book)
2020
mms
Nacke, R.
Voltage dependent interfacial magnetism in multilayer systems
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, December 2020 (thesis)
dlg
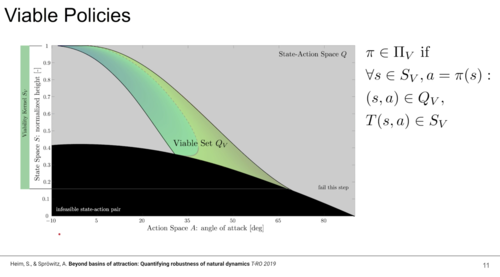
Heim, S., Badri-Spröwitz, A.
Beyond Basins of Attraction: Quantifying Robustness of Natural Dynamics
May 2020 (talk)
icm
Dertli, Denis
Nichtgleichgewichtsdynamik einer abgekühlten kritischen Flüssigkeit mit Oberflächenfeldern unterschiedlichen Vorzeichens
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, January 2020 (thesis)
am
ics
Marco, A., Rohr, A. V., Baumann, D., Hernández-Lobato, J. M., Trimpe, S.
Excursion Search for Constrained Bayesian Optimization under a Limited Budget of Failures
2020 (proceedings) In revision
avg
Janai, J., Güney, F., Behl, A., Geiger, A.
Computer Vision for Autonomous Vehicles: Problems, Datasets and State-of-the-Art
12(1-3), Foundations and Trends® in Computer Graphics and Vision, now Publishers Inc., Hanover, MA, 2020 (book)
2019
ei
Safavi, S., Logothetis, N., Besserve, M.
Multivariate coupling estimation between continuous signals and point processes
Neural Information Processing Systems 2019 - Workshop on Learning with Temporal Point Processes, December 2019 (talk)
ei
Lutz, P.
Automatic Segmentation and Labelling for Robot Table Tennis Time Series
Technical University Darmstadt, Germany, August 2019 (thesis)
icm
Pranjić, Daniel
Fluctuating interface with a pinning potential
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2019 (thesis)
ei
hi
ps
pi
Scientific Report 2016 - 2018
2019 (mpi_year_book)
mms
Keskinbora, K.
Prototyping Micro- and Nano-Optics with Focused Ion Beam Lithography
SL48, pages: 46, SPIE.Spotlight, SPIE Press, Bellingham, WA, 2019 (book)
icm
Beyer, David Bernhard
Controlling pattern formation in the confined Schnakenberg model
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2019 (thesis)
pf
Itzigehl, Selina
HPLC separation of ligand-exchanged gold clusters with atomic precision
Univ. of Stuttgart, 2019 (thesis)
2018
dlg
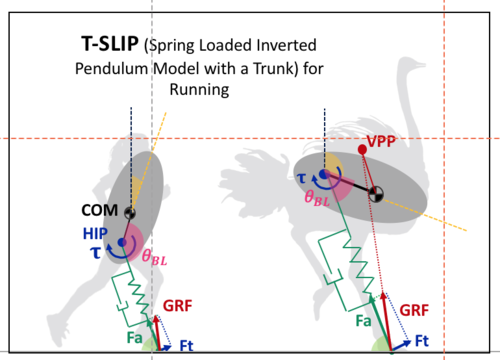
Drama, Ö.
Impact of Trunk Orientation for Dynamic Bipedal Locomotion
Dynamic Walking Conference, May 2018 (talk)
dlg
Richter, J.
Untersuchung und Charakterisierung von Teilelementen der Modifikation im Lumbosacralbereich von Vögeln
Hochschule Harz, 2018 (thesis)
icm
Maihöfer, Michael
Pattern forming systems under confinement
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
icm
Bebon, Rick
Electrostatic interaction between colloids with constant surface potentials at fluid interfaces
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
icm
Wilke, Moritz
Non-equilibrium dynamics of a binary solvent around heated colloidal particles
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
icm
Meiler, Tim
Monte Carlo study of colloidal structure formation at fluid interfaces
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
pf
Hornberger, Lea-Sophie
DNA-linked gold nanoclusters
Univ. of Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
pf
Wu, Z., Troll, J., Jeong, H., Qiang, W., Stang, M., Ziemssen, F., Wang, Z., Dong, M., Schnichels, S., Qiu, T., Fischer, P.
Nanorobots propel through the eye
Max Planck Society, 2018 (mpi_year_book)
icm
Sattler, Alexander
Surface structure of liquid crystals
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
pf
Vogt, Pascal
HPLC-Trennung von Gold-clustern
Univ. of Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
2017
ei
Peters, J., Janzing, D., Schölkopf, B.
Elements of Causal Inference - Foundations and Learning Algorithms
Adaptive Computation and Machine Learning Series, The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017 (book)
icm
Hölzl, Christian
Non-equilibrium forces after temperature quenches in ideal fluids with conserved density
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2017 (thesis)
pf
Troll, Jonas
Enzyme activity and transport in biological media
Univ. of Stuttgart, 2017 (thesis)
pi
Sitti, M.
Mobile Microrobotics
Mobile Microrobotics, The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 2017 (book)
pf
Segreto, Nico
Propulsion of magnetic colloids at low Reynolds number
Univ. of Stuttgart, 2017 (thesis)
zwe-sw
Bramlage, L.
Design of a visualization scheme for functional connectivity data of Human Brain
Hochschule Osnabrück - University of Applied Sciences, 2017 (thesis)
icm
Schmetzer, Timo
Electrostatic interaction between non-identical charged particles at an electrolyte interface
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2017 (thesis)
2016
ei
Ihler, A. T., Janzing, D.
Proceedings of the 32nd Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (UAI)
pages: 869 pages, AUAI Press, June 2016 (proceedings)
2015
ps
Gall, J., Gehler, P., Leibe, B.
Proceedings of the 37th German Conference on Pattern Recognition
Springer, German Conference on Pattern Recognition, October 2015 (proceedings)
ei
Besserve, M.
Causal Inference for Empirical Time Series Based on the Postulate of Independence of Cause and Mechanism
53rd Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, September 2015 (talk)
ei
Besserve, M.
Independence of cause and mechanism in brain networks
DALI workshop on Networks: Processes and Causality, April 2015 (talk)
am
ics
Doerr, A.
Policy Search for Imitation Learning
University of Stuttgart, January 2015 (thesis)
ei
Chaves, R., Majenz, C., Luft, L., Maciel, T., Janzing, D., Schölkopf, B., Gross, D.
Information-Theoretic Implications of Classical and Quantum Causal Structures
18th Conference on Quantum Information Processing (QIP), 2015 (talk)
ei
Foreman-Mackey, D., Hogg, D. W., Schölkopf, B.
The search for single exoplanet transits in the Kepler light curves
IAU General Assembly, 22, pages: 2258352, 2015 (talk)
2014
ps
Nowozin, S., Gehler, P. V., Jancsary, J., Lampert, C. H.
Advanced Structured Prediction
Advanced Structured Prediction, pages: 432, Neural Information Processing Series, MIT Press, November 2014 (book)