2023
dlg
Sarvestani, A., Ruppert, F., Badri-Spröwitz, A.
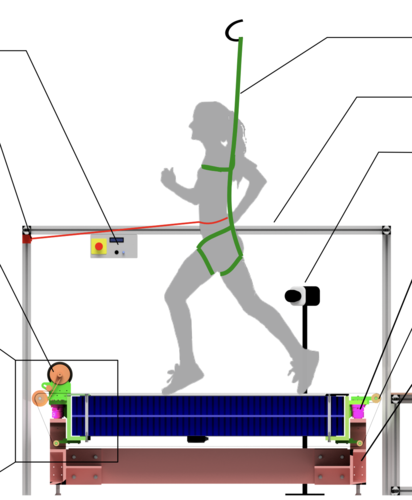
An Open-Source Modular Treadmill for Dynamic Force Measurement with Load Dependant Range Adjustment
2023 (unpublished) Submitted
2022
ei
Biester, L., Demszky, D., Jin, Z., Sachan, M., Tetreault, J., Wilson, S., Xiao, L., Zhao, J.
Proceedings of the Second Workshop on NLP for Positive Impact (NLP4PI)
Association for Computational Linguistics, December 2022 (proceedings)
ei
Schölkopf, B., Uhler, C., Zhang, K.
Proceedings of the First Conference on Causal Learning and Reasoning (CLeaR 2022)
177, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, PMLR, April 2022 (proceedings)
2021
ei
Field, A., Prabhumoye, S., Sap, M., Jin, Z., Zhao, J., Brockett, C.
Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on NLP for Positive Impact
Association for Computational Linguistics, August 2021 (proceedings)
2020
mms
Nacke, R.
Voltage dependent interfacial magnetism in multilayer systems
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, December 2020 (thesis)
ev
25th International Symposium on Vision, Modeling and Visualization, VMV 2020
(Editors: Jens Krüger and Matthias Nießner and Jörg Stückler), Eurographics Association, 2020 (proceedings)
am
ics
Marco, A., Rohr, A. V., Baumann, D., Hernández-Lobato, J. M., Trimpe, S.
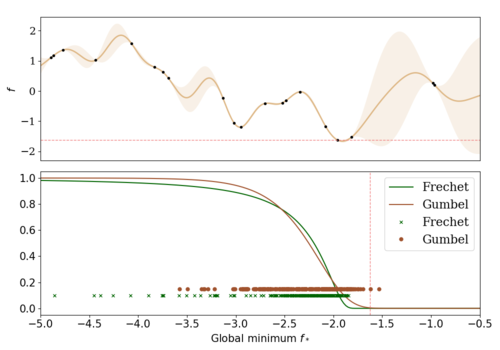
Excursion Search for Constrained Bayesian Optimization under a Limited Budget of Failures
2020 (proceedings) In revision
2019
ps
Dwivedi, S. K., Gupta, V., Mitra, R., Ahmed, S., Jain, A.
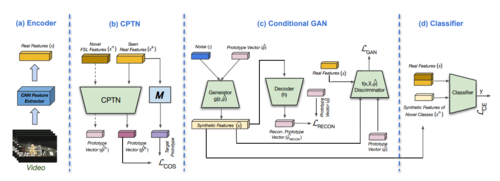
ProtoGAN: Towards Few Shot Learning for Action Recognition
Proc. International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Workshops, October 2019 (manual)
2016
ei
Ihler, A. T., Janzing, D.
Proceedings of the 32nd Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (UAI)
pages: 869 pages, AUAI Press, June 2016 (proceedings)
2015
ps
Gall, J., Gehler, P., Leibe, B.
Proceedings of the 37th German Conference on Pattern Recognition
Springer, German Conference on Pattern Recognition, October 2015 (proceedings)
am
ics
Doerr, A.
Policy Search for Imitation Learning
University of Stuttgart, January 2015 (thesis)
2014
ps
Tang, S., Andriluka, M., Milan, A., Schindler, K., Roth, S., Schiele, B.
Learning People Detectors for Tracking in Crowded Scenes.
2014, Scene Understanding Workshop (SUNw, CVPR workshop) (unpublished)
ei
Schmeißer, N.
Development of advanced methods for improving astronomical images
Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Germany, Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Germany, 2014 (diplomathesis)
2013
ei
pn
Schober, M.
Camera-specific Image Denoising
Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Germany, October 2013 (diplomathesis)
ei
Deisenroth, M., Szepesvári, C., Peters, J.
Proceedings of the 10th European Workshop on Reinforcement Learning, Volume 24
pages: 173, JMLR, European Workshop On Reinforcement Learning, EWRL, 2013 (proceedings)
2012
ei
Langs, G., Rish, I., Grosse-Wentrup, M., Murphy, B.
Machine Learning and Interpretation in Neuroimaging - Revised Selected and Invited Contributions
pages: 266, Springer, Heidelberg, Germany, International Workshop, MLINI, Held at NIPS, 2012, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 7263 (proceedings)
ei
Panagiotaki, E., O’Donnell, L., Schultz, T., Zhang, G.
MICCAI, Workshop on Computational Diffusion MRI, 2012 (electronic publication)
15th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Workshop on Computational Diffusion MRI , 2012 (proceedings)
ei
Hooge, J.
Automatische Seitenkettenzuordnung zur NMR Proteinstrukturaufklärung mittels ganzzahliger linearer Programmierung
University of Tübingen, Germany, 2012 (diplomathesis)
ei
pn
Klenske, E. D.
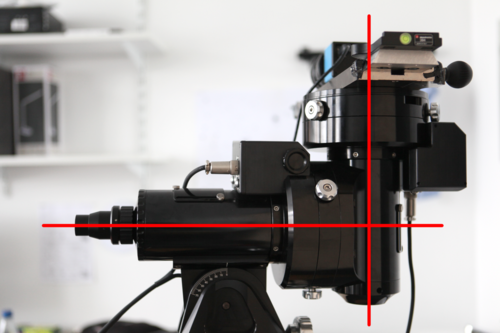
Nonparametric System Identification and Control for Periodic Error Correction in Telescopes
University of Stuttgart, 2012 (diplomathesis)
2011
ei
Kakade, S., von Luxburg, U.
JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings Volume 19: COLT 2011
pages: 834, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, USA, 24th Annual Conference on Learning Theory , June 2011 (proceedings)
am
11th IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids 2011), Bled, Slovenia, October 26-28, 2011
IEEE, 2011 (proceedings)
2010
ei
Zscheischler, J.
Inferring High-Dimensional Causal Relations using Free Probability Theory
Humboldt Universität Berlin, Germany, August 2010 (diplomathesis)
ei
Shelton, J.
Semi-supervised Subspace Learning and Application to Human Functional Magnetic Brain Resonance Imaging Data
Biologische Kybernetik, Eberhard Karls Universität, Tübingen, Germany, July 2010 (diplomathesis)
ei
Mantlik, F.
Quantitative Evaluation of MR-based Attenuation Correction for Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
Biologische Kybernetik, Universität Mannheim, Germany, March 2010 (diplomathesis)
ei
Guyon, I., Janzing, D., Schölkopf, B.
JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings: Volume 6
pages: 288, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, USA, Causality: Objectives and Assessment (NIPS Workshop) , February 2010 (proceedings)
ei
Rakitsch, B.
Finding Gene-Gene Interactions using Support Vector Machines
Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Germany, 2010 (diplomathesis)
ei
Köhler, R.
Detecting the mincut in sparse random graphs
Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Germany, 2010 (diplomathesis)
2009
ei
Mülling, K.
Motor Control and Learning in Table Tennis
Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Gerrmany, 2009 (diplomathesis)
ei
Drewe, P.
Hierarchical Clustering and Density Estimation Based on k-nearest-neighbor graphs
Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Germany, 2009 (diplomathesis)
2008
ei
Kober, J.
Reinforcement Learning for Motor Primitives
Biologische Kybernetik, University of Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany, August 2008 (diplomathesis)
ei
Peters, J.
Asymmetries of Time Series under Inverting their Direction
Biologische Kybernetik, University of Heidelberg, August 2008 (diplomathesis)
ei
Lespérance, Y., Lakemeyer, G., Peters, J., Pirri, F.
CogRob 2008: The 6th International Cognitive Robotics Workshop
Proceedings of the 6th International Cognitive Robotics Workshop (CogRob 2008), pages: 35, Patras University Press, Patras, Greece, 6th International Cognitive Robotics Workshop (CogRob), July 2008 (proceedings)
ei
Berens, P.
Pairwise Correlations and Multineuronal Firing Patterns in
Primary Visual Cortex
Biologische Kybernetik, Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany, April 2008 (diplomathesis)
ei
Schreiner, T.
Development and Application of a Python Scripting Framework for BCI2000
Biologische Kybernetik, Eberhard-Karls-Universität Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany, January 2008 (diplomathesis)
2007
ei
Jegelka, S.
Statistical Learning Theory Approaches to Clustering
Biologische Kybernetik, Eberhard-Karls-Universität Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany, November 2007 (diplomathesis)
ei
Schölkopf, B., Platt, J., Hofmann, T.
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 19: Proceedings of the 2006 Conference
Proceedings of the Twentieth Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2006), pages: 1690, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, USA, 20th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), September 2007 (proceedings)
ei
Biessmann, F.
Error Correcting Codes for the P300 Visual Speller
Biologische Kybernetik, Eberhard-Karls-Universität Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany, July 2007 (diplomathesis)
ei
Sinz, FH.
A priori Knowledge from Non-Examples
Biologische Kybernetik, Eberhard-Karls-Universität Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany, March 2007 (diplomathesis)
ei
Raths, C.
Development of a Brain-Computer Interface Approach Based on Covert Attention to Tactile Stimuli
University of Tübingen, Germany, University of Tübingen, Germany, January 2007 (diplomathesis)
ei
Hofmann, M.
A Machine Learning Approach for Estimating the Attenuation Map for a Combined PET/MR Scanner
Biologische Kybernetik, Max-Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics, Tübingen, Germany, 2007 (diplomathesis)
2006
ei
Nickisch, H.
Extraction of visual features from natural video data using Slow Feature Analysis
Biologische Kybernetik, Technische Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, September 2006 (diplomathesis)
ei
Deisenroth, MP.
An Online-Computation Approach to Optimal Finite-Horizon State-Feedback Control of Nonlinear Stochastic Systems
Biologische Kybernetik, Universität Karlsruhe (TH), Karlsruhe, Germany, August 2006 (diplomathesis)
ei
Nowozin, S.
Object Classification using Local Image Features
Biologische Kybernetik, Technical University of Berlin, Berlin, Germany, May 2006 (diplomathesis)
ei
Weiss, Y., Schölkopf, B., Platt, J.
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 18: Proceedings of the 2005 Conference
Proceedings of the 19th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2005), pages: 1676, MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, USA, 19th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), May 2006 (proceedings)
ei
Huhle, B.
Kernel PCA for Image Compression
Biologische Kybernetik, Eberhard-Karls-Universität, Tübingen, Germany, April 2006 (diplomathesis)
ei
Quinonero Candela, J., Dagan, I., Magnini, B., Lauria, F.
Machine Learning Challenges: evaluating predictive uncertainty, visual object classification and recognising textual entailment
Proceedings of the First Pascal Machine Learning Challenges Workshop on Machine Learning Challenges, Evaluating Predictive Uncertainty, Visual Object Classification and Recognizing Textual Entailment (MLCW 2005), pages: 462, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer, Heidelberg, Germany, First Pascal Machine Learning Challenges Workshop (MLCW), 2006 (proceedings)
2005
ei
Steinke, F.
Implicit Surfaces For Modelling
Human Heads
Biologische Kybernetik, Eberhard-Karls-Universität, Tübingen, September 2005 (diplomathesis)
ei
Nowozin, S.
Liver Perfusion using Level Set Methods
Biologische Kybernetik, Shanghai JiaoTong University, Shanghai, China, July 2005 (diplomathesis)
ei
Tanner, TG.
Efficient Adaptive Sampling of the Psychometric Function by Maximizing Information Gain
Biologische Kybernetik, Eberhard-Karls University Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany, May 2005 (diplomathesis)