2024
hi
Matthew, V., Simancek, R. E., Telepo, E., Machesky, J., Willman, H., Ismail, A. B., Schulz, A. K.
Empowering Change: The Role of Student Changemakers in Advancing Sustainability within Engineering Education
Proceedings of the American Society of Engineering Education (ASEE), June 2024, Victoria Matthew and Andrew K. Schulz contributed equally to this publication. (issue) In press
ei
Rahaman, N., Weiss, M., Wüthrich, M., Bengio, Y., Li, E., Pal, C., Schölkopf, B.
Language Models Can Reduce Asymmetry in Information Markets
arXiv:2403.14443, March 2024, Published as: Redesigning Information Markets in the Era of Language Models, Conference on Language Modeling (COLM) (techreport)
ev
Achterhold, J., Guttikonda, S., Kreber, J. U., Li, H., Stueckler, J.
Learning a Terrain- and Robot-Aware Dynamics Model for Autonomous Mobile Robot Navigation
CoRR abs/2409.11452, 2024, Preprint submitted to Robotics and Autonomous Systems Journal. https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.11452 (techreport) Submitted
lds
Eberhard, O., Vernade, C., Muehlebach, M.
A Pontryagin Perspective on Reinforcement Learning
Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, 2024 (techreport)
lds
Er, D., Trimpe, S., Muehlebach, M.
Distributed Event-Based Learning via ADMM
Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, 2024 (techreport)
ev
Baumeister, F., Mack, L., Stueckler, J.
Incremental Few-Shot Adaptation for Non-Prehensile Object Manipulation using Parallelizable Physics Simulators
CoRR abs/2409.13228, CoRR, 2024, Submitted to IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2025 (techreport) Submitted
2023
dlg
Sarvestani, A., Ruppert, F., Badri-Spröwitz, A.
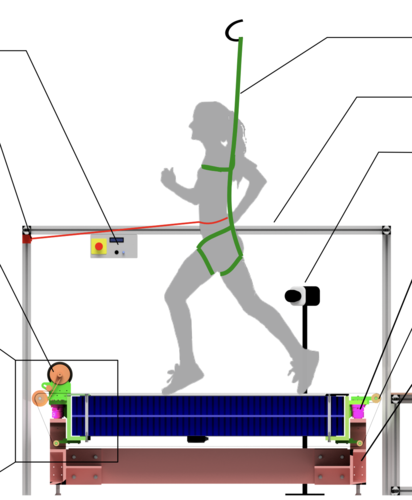
An Open-Source Modular Treadmill for Dynamic Force Measurement with Load Dependant Range Adjustment
2023 (unpublished) Submitted
ei
Berenz, V., Widmaier, F., Guist, S., Schölkopf, B., Büchler, D.
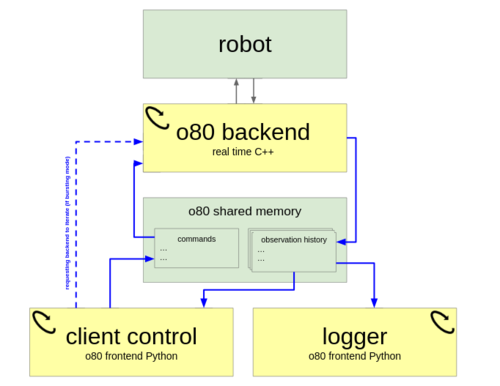
Synchronizing Machine Learning Algorithms, Realtime Robotic Control and Simulated Environment with o80
Robot Software Architectures Workshop (RSA) 2023, ICRA, 2023 (techreport)
2022
ei
Schölkopf, B.
Causality, causal digital twins, and their applications
Machine Learning for Science: Bridging Data-Driven and Mechanistic Modelling (Dagstuhl Seminar 22382), (Editors: Berens, Philipp and Cranmer, Kyle and Lawrence, Neil D. and von Luxburg, Ulrike and Montgomery, Jessica), September 2022 (talk)
dlg
Ruppert, F., Badri-Spröwitz, A.
Learning Plastic Matching of Robot Dynamics in Closed-Loop Central Pattern Generators: Data
Edmond, May 2022 (techreport)
dlg
pi
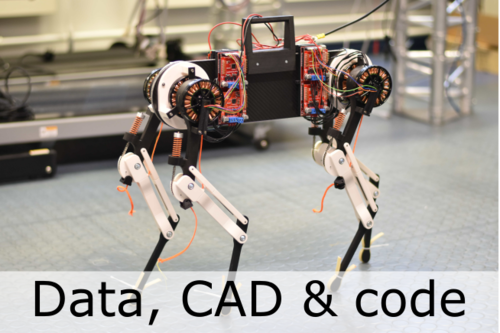
Badri-Spröwitz, A., Sarvestani, A. A., Sitti, M., Daley, M. A.
Data for BirdBot Achieves Energy-Efficient Gait with Minimal Control Using Avian-Inspired Leg Clutching
Edmond, March 2022 (techreport)
ev
Li, H., Stueckler, J.
Observability Analysis of Visual-Inertial Odometry with Online Calibration of Velocity-Control Based Kinematic Motion Models
abs/2204.06651, CoRR/arxiv, 2022 (techreport)
2021
ev
Strecke, M., Stückler, J.
Physically Plausible Tracking & Reconstruction of Dynamic Objects
KIT Science Week Scientific Conference & DGR-Days 2021, October 2021 (talk)
re
Heindrich, L., Consul, S., Stojcheski, J., Lieder, F.
Improving Human Decision-Making by Discovering Efficient Strategies for Hierarchical Planning
Tübingen, Germany, The first edition of Life Improvement Science Conference, June 2021 (talk) Accepted
re
Lieder, F., Prentice, M., Corwin-Renner, E.
Toward a Science of Effective Well-Doing
May 2021 (techreport)
re
Consul, S., Stojcheski, J., Felso, V., Lieder, F.
Optimal To-Do List Gamification for Long Term Planning
arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.06505, 2021 (techreport)
2020
mms
Nacke, R.
Voltage dependent interfacial magnetism in multilayer systems
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, December 2020 (thesis)
re
Stojcheski, J., Felso, V., Lieder, F.
Optimal To-Do List Gamification
ArXiv Preprint, 2020 (techreport)
dlg
Heim, S., Badri-Spröwitz, A.
Beyond Basins of Attraction: Quantifying Robustness of Natural Dynamics
May 2020 (talk)
ics
Baumann, D., Solowjow, F., Johansson, K. H., Trimpe, S.
Identifying Causal Structure in Dynamical Systems
2020 (techreport)
2019
ei
Safavi, S., Logothetis, N., Besserve, M.
Multivariate coupling estimation between continuous signals and point processes
Neural Information Processing Systems 2019 - Workshop on Learning with Temporal Point Processes, December 2019 (talk)
lds
Muehlebach, M.
The Silver Ratio and its Relation to Controllability
2019 (techreport)
2018
dlg
Drama, Ö.
Impact of Trunk Orientation for Dynamic Bipedal Locomotion
Dynamic Walking Conference, May 2018 (talk)
ev
Ma, L., Stueckler, J., Wu, T., Cremers, D.
Detailed Dense Inference with Convolutional Neural Networks via Discrete Wavelet Transform
arxiv, 2018, arXiv:1808.01834 (techreport)
lds
Muehlebach, M., D’Andrea, R.
On the Approximation of Constrained Linear Quadratic Regulator Problems and their Application to Model Predictive Control
2018 (techreport)
slt
Keriven, N., Garreau, D., Poli, I.
NEWMA: a new method for scalable model-free online change-point detection
2018 (techreport)
2016
am
ics
Ebner, S., Trimpe, S.
Supplemental material for ’Communication Rate Analysis for Event-based State Estimation’
Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, January 2016 (techreport)
ei
Castaneda, S., Katiyar, P., Russo, F., Calaminus, C., Disselhorst, J. A., Ziemann, U., Kohlhofer, U., Quintanilla-Martinez, L., Poli, S., Pichler, B. J.
Analysis of multiparametric MRI using a semi-supervised random forest framework allows the detection of therapy response in ischemic stroke
World Molecular Imaging Conference, 2016 (talk)
ei
Katiyar, P., Divine, M. R., Kohlhofer, U., Quintanilla-Martinez, L., Siegemund, M., Pfizenmaier, K., Kontermann, R., Pichler, B. J., Disselhorst, J. A.
Multi-view learning on multiparametric PET/MRI quantifies intratumoral heterogeneity and determines therapy efficacy
World Molecular Imaging Conference, 2016 (talk)
2015
am
ics
Trimpe, S.
Distributed Event-based State Estimation
Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, November 2015 (techreport)
ei
Besserve, M.
Causal Inference for Empirical Time Series Based on the Postulate of Independence of Cause and Mechanism
53rd Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, September 2015 (talk)
ei
Besserve, M.
Independence of cause and mechanism in brain networks
DALI workshop on Networks: Processes and Causality, April 2015 (talk)
am
ics
Doerr, A.
Policy Search for Imitation Learning
University of Stuttgart, January 2015 (thesis)
ei
Chaves, R., Majenz, C., Luft, L., Maciel, T., Janzing, D., Schölkopf, B., Gross, D.
Information-Theoretic Implications of Classical and Quantum Causal Structures
18th Conference on Quantum Information Processing (QIP), 2015 (talk)
ei
Castaneda, S. G., Katiyar, P., Russo, F., Disselhorst, J. A., Calaminus, C., Poli, S., Maurer, A., Ziemann, U., Pichler, B. J.
Assessment of brain tissue damage in the Sub-Acute Stroke Region by Multiparametric Imaging using [89-Zr]-Desferal-EPO-PET/MRI
World Molecular Imaging Conference, 2015 (talk)
ei
Divine, M. R., Harant, M., Katiyar, P., Disselhorst, J. A., Bukala, D., Aidone, S., Siegemund, M., Pfizenmaier, K., Kontermann, R., Pichler, B. J.
Early time point in vivo PET/MR is a promising biomarker for determining efficacy of a novel Db(\alphaEGFR)-scTRAIL fusion protein therapy in a colon cancer model
World Molecular Imaging Conference, 2015 (talk)
ei
Abbott, T., Abdalla, F. B., Allam, S., Amara, A., Annis, J., Armstrong, R., Bacon, D., Banerji, M., Bauer, A. H., Baxter, E., others,
Cosmology from Cosmic Shear with DES Science Verification Data
arXiv preprint arXiv:1507.05552, 2015 (techreport)
ei
Jarvis, M., Sheldon, E., Zuntz, J., Kacprzak, T., Bridle, S. L., Amara, A., Armstrong, R., Becker, M. R., Bernstein, G. M., Bonnett, C., others,
The DES Science Verification Weak Lensing Shear Catalogs
arXiv preprint arXiv:1507.05603, 2015 (techreport)
ei
Foreman-Mackey, D., Hogg, D. W., Schölkopf, B.
The search for single exoplanet transits in the Kepler light curves
IAU General Assembly, 22, pages: 2258352, 2015 (talk)
2014
ps
Freifeld, O., Hauberg, S., Black, M. J.
Model transport: towards scalable transfer learning on manifolds - supplemental material
(9), April 2014 (techreport)
ps
Ahmad, A., Amigoni, A., Awaad, I., Berghofer, J., Bischoff, R., Bonarini, A., Dwiputra, R., Fontana, G., Hegger, F., Hochgeschwender, N., Iocchi, L., Kraetzschmar, G., Lima, P., Matteucci, M., Nardi, D., Schiaffonati, V., Schneider, S.
RoCKIn@Work in a Nutshell
(FP7-ICT-601012 Revision 1.2), RoCKIn - Robot Competitions Kick Innovation in Cognitive Systems and Robotics, March 2014 (techreport)
ps
Ahmad, A., Amigoni, F., Awaad, I., Berghofer, J., Bischoff, R., Bonarini, A., Dwiputra, R., Fontana, G., Hegger, F., Hochgeschwender, N., Iocchi, L., Kraetzschmar, G., Lima, P., Matteucci, M., Nardi, D., Schneider, S.
RoCKIn@Home in a Nutshell
(FP7-ICT-601012 Revision 0.8), RoCKIn - Robot Competitions Kick Innovation in Cognitive Systems and Robotics, March 2014 (techreport)
ei
Besserve, M., Schölkopf, B., Logothetis, N. K.
Unsupervised identification of neural events in local field potentials
44th Annual Meeting of the Society for Neuroscience (Neuroscience), 2014 (talk)
ei
Besserve, M.
Quantifying statistical dependency
Research Network on Learning Systems Summer School, 2014 (talk)
ps
Tang, S., Andriluka, M., Milan, A., Schindler, K., Roth, S., Schiele, B.
Learning People Detectors for Tracking in Crowded Scenes.
2014, Scene Understanding Workshop (SUNw, CVPR workshop) (unpublished)
ei
Schmeißer, N.
Development of advanced methods for improving astronomical images
Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Germany, Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Germany, 2014 (diplomathesis)
ei
Divine, M. R., Disselhorst, J. A., Katiyar, P., Pichler, B. J.
Using a population based Gaussian Mixture Model on fused [18]F-FDG PET and DW-MRI images accurately segments the tumor microenvironment into clinically relevant compartments capable of guiding therapy
European Molecular Imaging Meeting, 2014 (talk)
ei
Janzing, D.
Causal Inference from Passive Observations
24th Summer School University of Jyväskylā, Finland, August, 2014 (talk)
2013
ei
pn
Schober, M.
Camera-specific Image Denoising
Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Germany, October 2013 (diplomathesis)