2024
hi
Matthew, V., Simancek, R. E., Telepo, E., Machesky, J., Willman, H., Ismail, A. B., Schulz, A. K.
Empowering Change: The Role of Student Changemakers in Advancing Sustainability within Engineering Education
Proceedings of the American Society of Engineering Education (ASEE), June 2024, Victoria Matthew and Andrew K. Schulz contributed equally to this publication. (issue) In press
2023
ei
Jenny, D.
Navigating the Ocean of Biases: Political Bias Attribution in Language Models via Causal Structures
ETH Zurich, Switzerland, November 2023, external supervision (thesis)
dlg
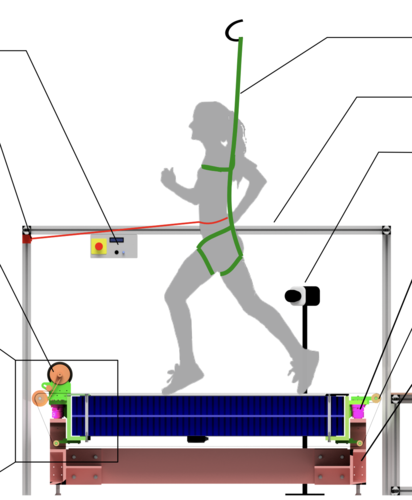
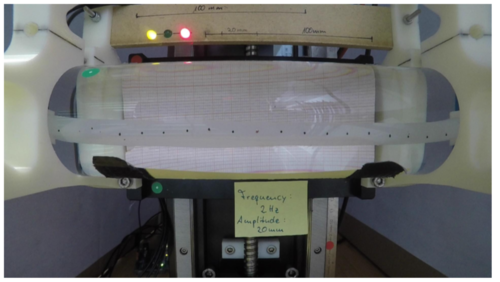
Sarvestani, A., Ruppert, F., Badri-Spröwitz, A.
An Open-Source Modular Treadmill for Dynamic Force Measurement with Load Dependant Range Adjustment
2023 (unpublished) Submitted
2020
mms
Nacke, R.
Voltage dependent interfacial magnetism in multilayer systems
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, December 2020 (thesis)
icm
Dertli, Denis
Nichtgleichgewichtsdynamik einer abgekühlten kritischen Flüssigkeit mit Oberflächenfeldern unterschiedlichen Vorzeichens
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, January 2020 (thesis)
2019
ei
Lutz, P.
Automatic Segmentation and Labelling for Robot Table Tennis Time Series
Technical University Darmstadt, Germany, August 2019 (thesis)
icm
Pranjić, Daniel
Fluctuating interface with a pinning potential
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2019 (thesis)
icm
Beyer, David Bernhard
Controlling pattern formation in the confined Schnakenberg model
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2019 (thesis)
pf
Itzigehl, Selina
HPLC separation of ligand-exchanged gold clusters with atomic precision
Univ. of Stuttgart, 2019 (thesis)
2018
dlg
Richter, J.
Untersuchung und Charakterisierung von Teilelementen der Modifikation im Lumbosacralbereich von Vögeln
Hochschule Harz, 2018 (thesis)
icm
Maihöfer, Michael
Pattern forming systems under confinement
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
icm
Bebon, Rick
Electrostatic interaction between colloids with constant surface potentials at fluid interfaces
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
icm
Wilke, Moritz
Non-equilibrium dynamics of a binary solvent around heated colloidal particles
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
icm
Meiler, Tim
Monte Carlo study of colloidal structure formation at fluid interfaces
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
pf
Hornberger, Lea-Sophie
DNA-linked gold nanoclusters
Univ. of Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
icm
Sattler, Alexander
Surface structure of liquid crystals
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
pf
Vogt, Pascal
HPLC-Trennung von Gold-clustern
Univ. of Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
2017
icm
Hölzl, Christian
Non-equilibrium forces after temperature quenches in ideal fluids with conserved density
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2017 (thesis)
pf
Troll, Jonas
Enzyme activity and transport in biological media
Univ. of Stuttgart, 2017 (thesis)
pf
Segreto, Nico
Propulsion of magnetic colloids at low Reynolds number
Univ. of Stuttgart, 2017 (thesis)
zwe-sw
Bramlage, L.
Design of a visualization scheme for functional connectivity data of Human Brain
Hochschule Osnabrück - University of Applied Sciences, 2017 (thesis)
icm
Schmetzer, Timo
Electrostatic interaction between non-identical charged particles at an electrolyte interface
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2017 (thesis)
2015
am
ics
Doerr, A.
Policy Search for Imitation Learning
University of Stuttgart, January 2015 (thesis)
2014
ps
Tang, S., Andriluka, M., Milan, A., Schindler, K., Roth, S., Schiele, B.
Learning People Detectors for Tracking in Crowded Scenes.
2014, Scene Understanding Workshop (SUNw, CVPR workshop) (unpublished)
ei
Schmeißer, N.
Development of advanced methods for improving astronomical images
Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Germany, Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Germany, 2014 (diplomathesis)
2013
ei
pn
Schober, M.
Camera-specific Image Denoising
Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Germany, October 2013 (diplomathesis)
2012
ei
Hooge, J.
Automatische Seitenkettenzuordnung zur NMR Proteinstrukturaufklärung mittels ganzzahliger linearer Programmierung
University of Tübingen, Germany, 2012 (diplomathesis)
ei
pn
Klenske, E. D.
Nonparametric System Identification and Control for Periodic Error Correction in Telescopes
University of Stuttgart, 2012 (diplomathesis)
2010
ei
Zscheischler, J.
Inferring High-Dimensional Causal Relations using Free Probability Theory
Humboldt Universität Berlin, Germany, August 2010 (diplomathesis)
ei
Shelton, J.
Semi-supervised Subspace Learning and Application to Human Functional Magnetic Brain Resonance Imaging Data
Biologische Kybernetik, Eberhard Karls Universität, Tübingen, Germany, July 2010 (diplomathesis)
ei
Mantlik, F.
Quantitative Evaluation of MR-based Attenuation Correction for Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
Biologische Kybernetik, Universität Mannheim, Germany, March 2010 (diplomathesis)
ei
Rakitsch, B.
Finding Gene-Gene Interactions using Support Vector Machines
Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Germany, 2010 (diplomathesis)
ei
Zwießele, M.
Detecting and modeling time shifts in microarray time series data applying Gaussian processes
Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Germany, 2010 (thesis)
ei
Köhler, R.
Detecting the mincut in sparse random graphs
Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Germany, 2010 (diplomathesis)
2009
ei
Mülling, K.
Motor Control and Learning in Table Tennis
Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Gerrmany, 2009 (diplomathesis)
ei
Drewe, P.
Hierarchical Clustering and Density Estimation Based on k-nearest-neighbor graphs
Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Germany, 2009 (diplomathesis)
2008
ei
Kober, J.
Reinforcement Learning for Motor Primitives
Biologische Kybernetik, University of Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany, August 2008 (diplomathesis)
ei
Peters, J.
Asymmetries of Time Series under Inverting their Direction
Biologische Kybernetik, University of Heidelberg, August 2008 (diplomathesis)
ei
Berens, P.
Pairwise Correlations and Multineuronal Firing Patterns in
Primary Visual Cortex
Biologische Kybernetik, Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany, April 2008 (diplomathesis)
ei
Schreiner, T.
Development and Application of a Python Scripting Framework for BCI2000
Biologische Kybernetik, Eberhard-Karls-Universität Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany, January 2008 (diplomathesis)
2007
ei
Jegelka, S.
Statistical Learning Theory Approaches to Clustering
Biologische Kybernetik, Eberhard-Karls-Universität Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany, November 2007 (diplomathesis)
ei
Biessmann, F.
Error Correcting Codes for the P300 Visual Speller
Biologische Kybernetik, Eberhard-Karls-Universität Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany, July 2007 (diplomathesis)
ei
Sinz, FH.
A priori Knowledge from Non-Examples
Biologische Kybernetik, Eberhard-Karls-Universität Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany, March 2007 (diplomathesis)
ei
Raths, C.
Development of a Brain-Computer Interface Approach Based on Covert Attention to Tactile Stimuli
University of Tübingen, Germany, University of Tübingen, Germany, January 2007 (diplomathesis)
ei
Hofmann, M.
A Machine Learning Approach for Estimating the Attenuation Map for a Combined PET/MR Scanner
Biologische Kybernetik, Max-Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics, Tübingen, Germany, 2007 (diplomathesis)
2006
ei
Nickisch, H.
Extraction of visual features from natural video data using Slow Feature Analysis
Biologische Kybernetik, Technische Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, September 2006 (diplomathesis)
ei
Deisenroth, MP.
An Online-Computation Approach to Optimal Finite-Horizon State-Feedback Control of Nonlinear Stochastic Systems
Biologische Kybernetik, Universität Karlsruhe (TH), Karlsruhe, Germany, August 2006 (diplomathesis)
ei
Nowozin, S.
Object Classification using Local Image Features
Biologische Kybernetik, Technical University of Berlin, Berlin, Germany, May 2006 (diplomathesis)
ei
Huhle, B.
Kernel PCA for Image Compression
Biologische Kybernetik, Eberhard-Karls-Universität, Tübingen, Germany, April 2006 (diplomathesis)
2005
ei
Steinke, F.
Implicit Surfaces For Modelling
Human Heads
Biologische Kybernetik, Eberhard-Karls-Universität, Tübingen, September 2005 (diplomathesis)