2024
ei
Ortu, F.
Interpreting How Large Language Models Handle Facts and Counterfactuals through Mechanistic Interpretability
University of Trieste, Italy, March 2024 (mastersthesis)
2023
ei
Sakenyte, U.
Denoising Representation Learning for Causal Discovery
Université de Genèva, Switzerland, December 2023, external supervision (mastersthesis)
ei
Kofler, A.
Efficient Sampling from Differentiable Matrix Elements
Technical University of Munich, Germany, September 2023 (mastersthesis)
ei
Spieler, A. M.
Intrinsic complexity and mechanisms of expressivity of cortical neurons
University of Tübingen, Germany, March 2023 (mastersthesis)
lds
ei
Kladny, K.
CausalEffect Estimation by Combining Observational and Interventional Data
ETH Zurich, Switzerland, February 2023 (mastersthesis)
ei
Qui, Z.
Towards Generative Machine Teaching
Technical University of Munich, Germany, February 2023 (mastersthesis)
ei
Schneider, F.
ArchiSound: Audio Generation with Diffusion
ETH Zurich, Switzerland, January 2023, external supervision (mastersthesis)
ei
Dittrich, A.
Generation and Quantification of Spin in Robot Table Tennis
University of Stuttgart, Germany, January 2023 (mastersthesis)
dlg
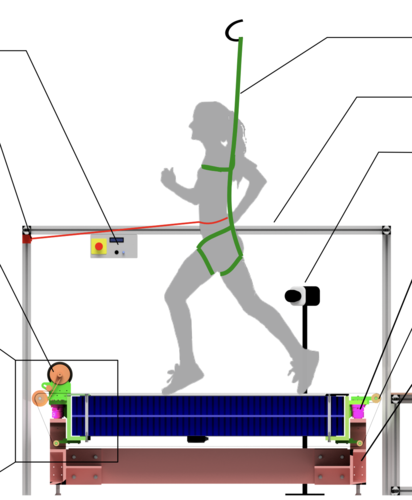
Sarvestani, A., Ruppert, F., Badri-Spröwitz, A.
An Open-Source Modular Treadmill for Dynamic Force Measurement with Load Dependant Range Adjustment
2023 (unpublished) Submitted
ei
Jin, Z., Mihalcea, R.
Natural Language Processing for Policymaking
In Handbook of Computational Social Science for Policy, pages: 141-162, 7, (Editors: Bertoni, E. and Fontana, M. and Gabrielli, L. and Signorelli, S. and Vespe, M.), Springer International Publishing, 2023 (inbook)
2022
pf
Qiu, T., Jeong, M., Goyal, R., Kadiri, V., Sachs, J., Fischer, P.
Magnetic Micro-/Nanopropellers for Biomedicine
In Field-Driven Micro and Nanorobots for Biology and Medicine, pages: 389-410, 16, (Editors: Sun, Y. and Wang, X. and Yu, J.), Springer, Cham, 2022 (inbook)
re
Lieder, F., Prentice, M.
Life Improvement Science
In Encyclopedia of Quality of Life and Well-Being Research, Springer, November 2022 (inbook)
ei
Liang, W.
Investigating Independent Mechanisms in Neural Networks
Université Paris-Saclay, France, October 2022 (mastersthesis)
ei
Keidar, D.
Modeling subgroup differences in fMRI data: disentangling subgroup-specific responses from shared ones
ETH Zurich, Switzerland, October 2022 (mastersthesis)
ei
Feil, M.
Multi-Target Multi-Object Manipulation using Relational Deep Reinforcement Learning
Technnical University Munich, Germany, September 2022 (mastersthesis)
ei
Sliwa, J.
Independent Mechanism Analysis for High Dimensions
University of Tübingen, Germany, September 2022, (Graduate Training Centre of Neuroscience) (mastersthesis)
ei
Dominguez-Olmedo, R.
On the Adversarial Robustness of Causal Algorithmic Recourse
University of Tübingen, Germany, August 2022 (mastersthesis)
ei
Ghosh, S.
Independent Mechanism Analysis in High-Dimensional Observation Spaces
ETH Zurich, Switzerland, June 2022 (mastersthesis)
ei
Peters, J., Bauer, S., Pfister, N.
Causal Models for Dynamical Systems
In Probabilistic and Causal Inference: The Works of Judea Pearl, pages: 671-690, 1, Association for Computing Machinery, 2022 (inbook)
ei
plg
Karimi, A. H., von Kügelgen, J., Schölkopf, B., Valera, I.
Towards Causal Algorithmic Recourse
In xxAI - Beyond Explainable AI: International Workshop, Held in Conjunction with ICML 2020, July 18, 2020, Vienna, Austria, Revised and Extended Papers, pages: 139-166, (Editors: Holzinger, Andreas and Goebel, Randy and Fong, Ruth and Moon, Taesup and Müller, Klaus-Robert and Samek, Wojciech), Springer International Publishing, 2022 (inbook)
ei
Salewski, L., Koepke, A. S., Lensch, H. P. A., Akata, Z.
CLEVR-X: A Visual Reasoning Dataset for Natural Language Explanations
In xxAI - Beyond Explainable AI: International Workshop, Held in Conjunction with ICML 2020, July 18, 2020, Vienna, Austria, Revised and Extended Papers, pages: 69-88, (Editors: Holzinger, Andreas and Goebel, Randy and Fong, Ruth and Moon, Taesup and Müller, Klaus-Robert and Samek, Wojciech), Springer International Publishing, 2022 (inbook)
ei
Schölkopf, B.
Causality for Machine Learning
In Probabilistic and Causal Inference: The Works of Judea Pearl, pages: 765-804, 1, Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 2022 (inbook)
mms
Miller, M.
Voltage dependent investigations on the spin polarization of layered heterostructues
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2022 (mastersthesis)
2021
ei
Scherrer, N.
Learning Neural Causal Models with Active Interventions
ETH Zurich, Switzerland, November 2021 (mastersthesis)
ei
Bing, S.
HealthGen: Conditional Generation of Realistic Medical Time Series with Informative Missingness
ETH Zurich, Switzerland, October 2021 (mastersthesis)
ei
Lanzillotta, G.
Study of the Interventional Consistency of Autoencoders
ETH Zurich, Switzerland, October 2021 (mastersthesis)
ei
Mambelli, D.
Training with Few to Manipulate Many. On OOD generalization in relational reinforcement learning
ETH Zurich, Switzerland, October 2021 (mastersthesis)
rm
Purnendu, , Novack, S., Acome, E., Alistar, M., Keplinger, C., Gross, M. D., Bruns, C., Leithinger, D.
Electriflow: Augmenting Books With Tangible Animation Using Soft Electrohydraulic Actuators
In ACM SIGGRAPH 2021 Labs, pages: 1-2, Association for Computing Machinery, SIGGRAPH 2021, August 2021 (inbook)
hi
Krauthausen, F.
Robotic Surgery Training in AR: Multimodal Record and Replay
pages: 1-147, University of Stuttgart, Stuttgart, May 2021, Study Program in Software Engineering (mastersthesis)
mms
Alten, F.
Direct detection of spin Hall effect induced torques in platinum/ferromagnetic bilayer systems
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, January 2021 (mastersthesis)
pi
Sitti, M., Liimatainen, V.
Method of making one or more fibrils, computer implemented method of simulating an adhesive force of one or more fibrils and fibril
2021, EP Prio. Patent App. 21 162 253.5 (mpi_year_book)
pio
Zottino, N.
Community detection in heterogeneously attributed networks
Politecnico di Torino, 2021 (mastersthesis)
ei
hi
ps
pi
rm
Scientific Report 2016 - 2021
2021 (mpi_year_book)
minibot
Chu, X., Wang, W., Müller, J., Schöning, H. V., Liu, Y., Weigand, B.
Turbulence Modulation and Energy Transfer in Turbulent Channel Flow Coupled with One-Side Porous Media
In High Performance Computing in Science and Engineering’20, pages: 373-386, Springer, 2021 (incollection)
2020
mms
Nacke, R.
Voltage dependent interfacial magnetism in multilayer systems
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, December 2020 (thesis)
mms
Sauter, R.
Hydromagnonics: Manipulation of magnonic systems with hydrogen
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, December 2020 (mastersthesis)
ei
Ahmed, O.
A Robotic Manipulation Benchmark for Causal Structure and Transfer Learning
ETH Zurich, Switzerland, October 2020 (mastersthesis)
ei
DuMont Schütte, A.
A Comprehensive Benchmark Evaluation of Synthetic Data Generation for Biomedical Imaging
ETH Zurich, Switzerland, October 2020 (mastersthesis)
ei
Cacioppo, A.
Deep learning for the parameter estimation of tight-binding Hamiltonians
University of Roma, La Sapienza, Italy, May 2020 (mastersthesis)
ei
Zecevic, M.
Learning Algorithms, Invariances, and the Real World
Technical University of Darmstadt, Germany, April 2020 (mastersthesis)
mms
Bondorf, L.
Interaction of hydrogen isotopes with flexible metal-organic frameworks
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, February 2020 (mastersthesis)
pio
Lonardi, A.
Developing new methods for routing and optimal transport on networks
Università degli studi di Padova, 2020 (mastersthesis)
ev
Usenko, V., Stumberg, L. V., Stückler, J., Cremers, D.
TUM Flyers: Vision-Based MAV Navigation for Systematic Inspection of Structures
In Bringing Innovative Robotic Technologies from Research Labs to Industrial End-users: The Experience of the European Robotics Challenges, 136, pages: 189-209, Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics, Springer International Publishing, 2020 (inbook)
pio
Lorenzo Ferretti
Edge-Disjoint Path Problem on Stochastic Block Models through Message Passing
Sapienza Università di Roma, 2020 (mastersthesis)
icm
Popescu, M. N., Uspal, W. E.
Adopting the Boundary Homogenization Approximation from Chemical Kinetics to Motile Chemically Active Particles
In Chemical Kinetics, pages: 517-540, (Editors: Lindenberg, Katja and Metzler, Ralf and Oshanin, Gleb), World Scientific, New Jersey, NJ, 2020 (incollection)
ncs
Thies, J., Zollhöfer, M., Theobalt, C., Stamminger, M., Nießner, M.
Image-guided Neural Object Rendering
In International Conference on Learning Representations, 2020 (incollection)
pf
Baldauf, A.
Colloidal particles supporting urase activity
Univ. of Stuttgart, 2020 (mastersthesis)
pf
Palagi, S.
Soft Microrobots Based on Photoresponsive Materials
In Mechanically Responsive Materials for Soft Robotics, pages: 327-362, (Editors: Koshima, Hideko), Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2020 (incollection)
pf
Bochert, I.
Diffusion studies on biomolecules by NMR
Univ. of Stuttgart, 2020 (mastersthesis)
2019
pio
Emanuele Pigani
Analysis and modelling of information ecosystems
Università degli studi di Padova, October 2019 (mastersthesis)